UBT Consultants & UPRs
Help Video
How to Find UBT Basics on the LMP Website
LMP Website Overview
How to Find How-To Guides
This short animated video explains how to find and use our powerful how-to guides
How to Find and Use Team-Tested Practices
Does your team want to improve service? Or clinical quality? If you don't know where to start, check out the team-tested practices on the LMP website. This short video shows you how.
How to Use the Search Function on the LMP Website
Having trouble using the search function? Check out this short video to help you search like a pro!
How to Find the Tools on the LMP Website
Need to find a checklist, template or puzzle? Don't know where to start? Check out this short video to find the tools you need on the LMP website with just a few clicks.
Humans of Partnership:
Giving Equal Opportunity to All
Deck: Denver contact center team clarifies selection process for leadership role
For customer service representatives, the role of “chat captain” is a plum post—a leadership position that allows a rep to develop expertise and offers a break from the phones. But at the Member Service Contact Center (MSCC) in Denver, uncertainty about how the captains were chosen was breeding low morale.
The chat captains specialize in a range of topics, from Medicare and Medicaid to specific health plans for regions including Colorado, the Northwest, and Northern and Southern California. When a co-worker is on the phone with a member and doesn’t have an answer to a question, he or she can message a chat captain and get information quickly, before the call ends—helping provide great service to that member.
But the process managers used to select the 25 chat captains wasn’t clear, so the 400 customer service representatives didn’t know what they needed to do to qualify for the position.
‘Problems Are Only Opportunities…’
Deck: Solving disagreements using partnership tools frees teams to focus on improving quality and service
Management and union representatives in Southern California were at odds when they gathered in March 2015 to settle a UNAC/UHCP grievance over the working conditions of registered nurses in Home Health, Hospice and Palliative Care.
Because of the dispute’s complexity and scope, involving nurses regionwide, it was moved from the grievance process into issue resolution.
“When they started, it was the Mason-Dixon Line. It was management on one side and labor on the other side,” recalls Marcia Meredith, who works as a neutral facilitator in Southern California. She gets called on when “sticky and contentious” issues come up involving the Labor Management Partnership, which is celebrating its 20th anniversary this year. “It was pretty tense.”
Months later, managers and union representatives were working side by side, forging consensus on key issues.
Key to their success was the issue resolution (IR) process spelled out as part of the partnership between the Coalition of Kaiser Permanente Unions and Kaiser Permanente. It incorporates interest-based problem solving (IBPS) and consensus decision making (CDM) to provide a framework for settling disagreements collaboratively—providing a modern-day take on Henry J. Kaiser's line, “Problems are only opportunities in work clothes.”
Bringing order to chaos
They also benefited from the fact that Southern California—after watching people struggle for months and sometimes years without resolving their problems—recently had clarified how the process was to be used and had added a clear path for escalating issues.
“Issue resolution helps you focus on what the problem is and the possible solutions,” says Meredith.
The nurses and managers eventually agreed to make changes to assignment workflows, improve communication and enhance training opportunities for frontline workers. “They came up with good things that they’re still using,” says Meredith.
Crafting Southern California's appeals process took months of hard work. Key stakeholders included regional LMP Council members, coalition union leaders and Human Resources administrators.
Before escalation changes took effect on Jan. 1, 2015, the issue resolution process had tended to spin out of control.
‘It was like the Wild West’
“It was like the Wild West. Everybody did their own thing,” recalls Ilda Luna, an SEIU-UHW service representative for Glendale Medical Offices in Southern California.
Alex Espinoza, the Coalition of Kaiser Permanente Union’s national coordinator for Southern California, agrees.
“People would email whomever they thought would resolve the issue,” he says, citing examples of individuals who leapfrogged layers of union and management intervention to appeal directly to leaders at the national level.
During national bargaining in 2015, Southern California representatives shared the region’s appeals process, and the subgroup working on the issue recommended a similar process be created in every region.
The approach calls for resolving issues at the lowest possible level. For stubborn disagreements, there is now a standardized process for escalation the aggrieved parties can turn to, with 30-day deadlines for resolution at every step of the way.
In Southern California, for issues that can’t be resolved at the facility level, a nine-member regional SWAT team made up of management and union representatives serves as a court of last resort before the matter heads to national leaders.
But since the process was adopted two years ago and local LMP Councils and union leaders were educated about how to use it, no issue has been referred to the regional team.
That’s good news, says Maryanne Malzone Miller, senior director of Human Resources in Southern California and a SWAT team member.
“I like to believe we’re pushing it to the level where it should be resolved,” Miller says.
“It’s a success,” agrees Espinoza, also a SWAT team member. “Folks are engaged and are talking to each other.”
Transport Team Tackles Turnaround Times
Deck: Issue resolution helps untangle a web of problems
Patient transportation workers at Sunnyside Medical Center in Portland were in a tough spot: No matter how hard they scrambled, they were constantly running late to pick up patients.
Some of the challenges were clear. The transport workers, members of SEIU Local 49, are qualified to backfill certified nursing assistant positions—and short-staffed nursing units were calling on them to do just that.
In addition, a new computer-based dispatch system had automated patient transfer requests but required fewer dispatchers. The resulting staff upheaval, along with rumors about changes to their certification requirements, threw the unit-based team into turmoil.
Delays and frustration
Amid frustration and mounting delays—the team was only infrequently meeting its goal of getting to the patient within 15 minutes—improvement advisor Lolita Burnette worked with the team to resolve its issues. To better understand its challenges, she created a process map of the team’s workflow. That turned up a variety of obstacles that were thwarting efforts to improve times.
“Shadowing the team was an eye-opener. We discovered issues that were immediately actionable,” says Burnette. Because of the complexity of the situation, team members called for an issue resolution to identify solutions.
“My staff are really concerned about their patients. They had valid concerns about what was hindering our on-time performance,” says Marta Witsoe, the team’s management co-lead.
The issue resolution took place from July to September last year and helped further identify issues that were impacting on-time performance, as well as showing how delays affected imaging appointments and patient satisfaction.
As it tracked the source of delays, the team discovered that often, the patient was not ready to be moved when transporters arrived. The patient might need a different gown for imaging, or needed to take medications before being moved. Making matters worse, nurses and other staff members had gotten accustomed to transport arriving late and often put in orders ahead of time. But if the transport person arrived on time, the resulting delay had a domino effect, making it more difficult to be on time for subsequent transport requests.
New equipment, new hires
As a result of the issue resolution, the team is partnering with other units to become more efficient. Several improvements are being worked on simultaneously to increase productivity and overall satisfaction—and the team is confident the changes will lead to improved metrics.
In perhaps the most significant change, hospital leadership agreed to hire additional transport staff. The new positions are dedicated to support the Emergency Department, a frequent source of patient transfer requests.
“With time and commitment,” says Esther Logan, the team’s union co-lead, “we agreed upon issues that needed to be addressed within the department.”
Olivia Devers, a labor partner with SEIU Local 49, added, “This IR process was the most positive that I have witnessed in many years—the team and management worked in true partnership from start to finish.”
From the Desk of Henrietta: A Fresh Look at Problems
Henry J. Kaiser, Kaiser Permanente’s co-founder, famously told fellow industrialist Warren Bechtel, “Problems are only opportunities in work clothes.”
If you work with unit-based teams—as a co-lead, consultant or sponsor—you might be rolling your eyes right now and thinking, “Well, if that’s true, I sure have a lot of ‘opportunities.’ Grrr!”
When a team has problems, it’s difficult—if not impossible—to boldly improve service and quality for our health plan members. Especially if problems linger and fester, eroding trust and goodwill. These can depress morale and even endanger patients.
Lucky for us, the leaders of Kaiser Permanente and the Coalition of Kaiser Permanente Unions had the moral imagination more than two decades ago to envision a better way to solve problems. Together, they formed what would become our Labor Management Partnership.
As we celebrate our partnership’s 20th anniversary this year, we can look back and see how we have built the tools, structures and culture that support this alternative vision of how workers and employers can interact.
One of those tools is issue resolution. As you will see in the stories that follow, this process bypasses more traditional forms of problem solving in favor of going deeper to really uncover the source of the difficulty. By doing that, union members, managers and physicians not only can preserve their working relationships, but also make them stronger. This, in turn, fosters innovation and improvement.
Now that sounds like a great opportunity.
TOOLS
Differences Between Grievances and Issue Resolution
Format:
PDF (color or black and white)
Size:
8.5" x 11"
Intended audience:
Any union and management leaders involved in solving workplace problems.
Best used:
Use this chart to decide whether a grievance or issue resolution would be the best method for solving a sticky situation.
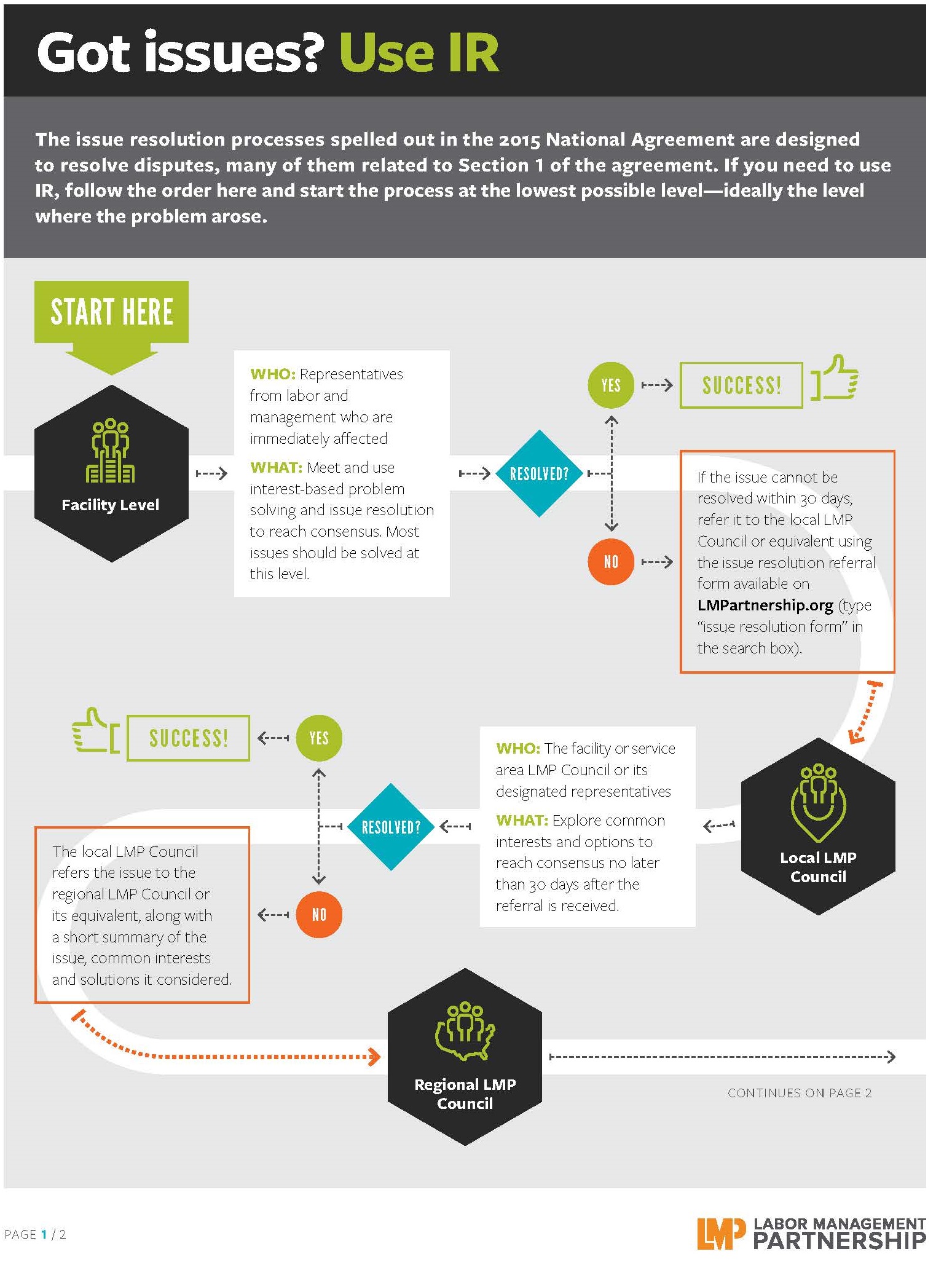
TOOLS
Issue Resolution Step by Step
Format:
PDF (color or black and white)
Size:
Two pages, 8.5" x 11"
Intended audience:
UBT co-leads, consultants and sponsors, as well as facility-level leaders.
Best used:
This infographic is best used to understand the issue resolution process, step by step.
Choosing to Work Positively
- Placing a Gratitude Jar in the entrance of the department (a prominent position)
- “Planting” a Gratitude Tree on a wall
- Buying playful fruit-shaped sticky notes to write their gratitude messages and post on the tree
What can your team do to measure and reduce stress?
How-To Guide: UBT Successful Practices
Use the posters and tools at right in presentations or meetings to help your teams overcome barriers, compare results and reach high performance.
The PowerPoint slides ("These Results Prove It's Working") show examples of unit-based teams from every region making a difference for KP members and patients.
Borrow from the ideas on this page to inspire your team, convince doubters to come on board, and identify projects and practices that have worked for others.